QUAD TEAR
(and Extensor Mechanism Injuries)
our website is for educational purposes only. the information provided is not a substitution for seeing a medical doctor. for the treatment of a medical condition, see your doctor. we update the site frequently but medicine also changes frequently. thus the information on this site may not be current or accurate.
related talks: kneecap dislocation; broken knee, runners knee, broken kneecap, kneecap dislocation, hamstring tear
What is a Quad Tear (Extensor Mechanism Injury)?
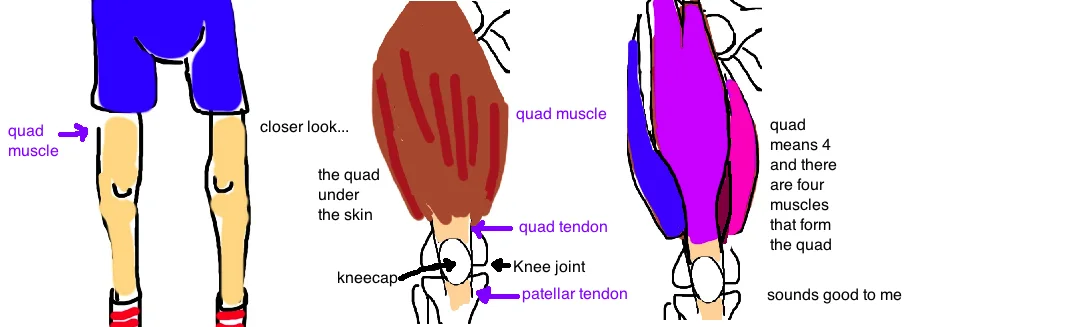
Our Quadraceps ("quad") muscle is acutually a few muscles ("quad" as in 4) that join together to form one large tendon which crosses the knee joint and attaches to the shin bone (tibia). Our quads straighten our leg. It opposes our hamstring muscles (which are located along the back of our leg and which bend our leg).
There are two types of Quad Injuries we will discuss here. A tear of the muscle fibers and a tear of the tendon.
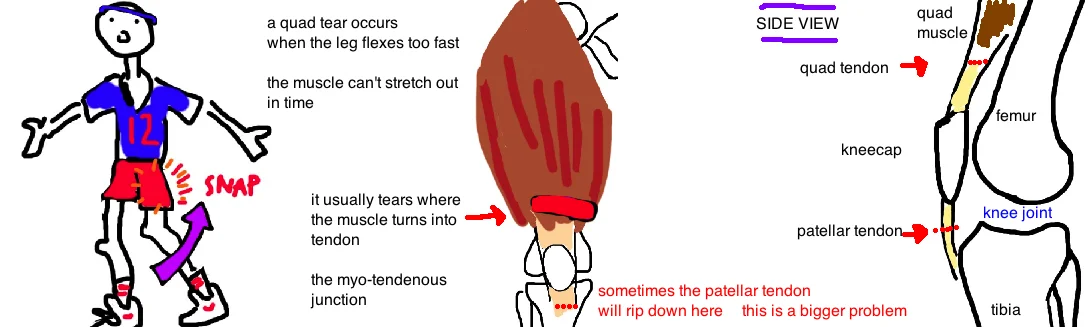
Our quad muscle is at risk of tearing when there is an imbalance between our hamstrings and quads. Some athletes strengthen some muscle groups more than others, this imbalance can put the "weaker" muscles at risk of injury. The quad muscle can tear if the knee flexes too fast causing the quad to stretched too fast (called eccentric loading). Its almost like stretching a rubber band: if you stretch it slowly, it expands to accommodate the applied force, but when you stretch it too quick, it just snaps because you havent given the fibers time to expand.
Diagnosing a Quad Tendon Tear (Extensor Mechanism Injury):
Someone with a Quad muscle tear reports significant pain in the front of the thigh, often accompanied by swelling and bruising. People usually remember the exact moment when they felt the onset of pain, most commonly while playing sports. Sometimes the muscle or tendon will tear completely and sometimes it will only partially tear. Its important for doctors to distinguish between the two because it affects treatment.
When examining the injured leg, doctors will as a person will be unable to hold their leg straight in the air because this tests the leg "extensor mechanism". If the quad is only strained or partially torn, the extensor mechanism should remain intact and you should be able to hold the leg in the air (it probably will be painful). If the quad tendon is completely torn, then the extensor mechanism will not work and you will be unable to hold the leg up against gravity. Additionally, in a complete tear, there is usually a gap just above the kneecap that can be felt through the skin because the torn tendon has retracted. In a partial tear there shouldnt be any gapping.
Many times, doctors will order an MRI to confirm a partial tear (and evaluate its severity), while a complete tear is usually diagnosed by clinical exam alone.
Treating a Quad Tendon Tear (Extensor Mechanism Injury):
The initial goal of treatment for a Quad muscle tears is to minimize bruising ("hematoma formation"). A muscle is has a significant blood flow (this allows rapid oxygen delivery to give power to a muscle) so when it tears, it can bleed a lot. A large collection of blood will be painful, and it can even cause abnormal bone formation within the muscle (this is called heterotopic ossification, or "HO") after a muscle tear. HO can cause long-term pain that may require surgery to remove. Therefore within the first 2 days, the muscle is actually kept tight by holding the knee in full flexion, to minimize bleeding.
After this initial treatment, a physical therapy routine will gradually return people to their pre-injury activity level.
Treatment of a Patellar tendon tear (the other part of the extensor mechanism: this attaches the kneecap to the shin bone) requires surgery. This tendon will not heal on its own, and surgery is needed to bring the two ends back together. After surgery, a persons leg is placed into a cast that keeps the leg fully straight for a few weeks to give the tendon enough time to heal.
What is the long term outcome?
The biggest concern in a Quad Tendon tear is the formation of heterotopic ossification. The muscle itself will heal well and typically returns to the pre-injury strength.
A Patellar tendon tear (the other part of our leg "extensor mechanism") does not heal consistently if left alone, and therefore needs surgery to place the two ends back together. The bigger concern with this injury is the strength of the repaired tendon. There is a risk for re-injury.
Reference
1) Siwek C, Rao J. Ruptures of the extensor mechanism of the knee joint. JBJS 1981; 63: 932-37. full article. patellar tendon <40, quad tendon >40. delay rx over 7 days worse outcomes: worse satisfaction, extensor lag, quad weakness.
2) Boublik M et al. Quadriceps tendon injuries in national football league players. Am J Sports Med 2013; 41: 1841-6. full article. 80% eccentric quad contraction, 80% reported return to preinjury activity level; but only 50% returned to nfl games.
3) Kannus P, Jozsa L. Histopathological changes preceding spontaneous rupture of a tendon: a controlled study of 891 patients. JBJS 1991; 73: 1507-25. full article. 97% of ruptured tendons have signs of degenerative tear.
) Rasul AT, Fischer DA. Primary repair of quadriceps tendon ruptures. CORR 1993; 289: 205-7. full article. upture occurs at bone-tendon jxn (in younger the tear occurs mid-tendon), all 17 pts had good-excellent outcomes.
5) Konrath GA et al. Outcomes following repair of quadriceps tendon ruptures. JOT 1998; 12: 273-9. full article. only 50% return to preactivity level after repair, overall good motion and daily function.