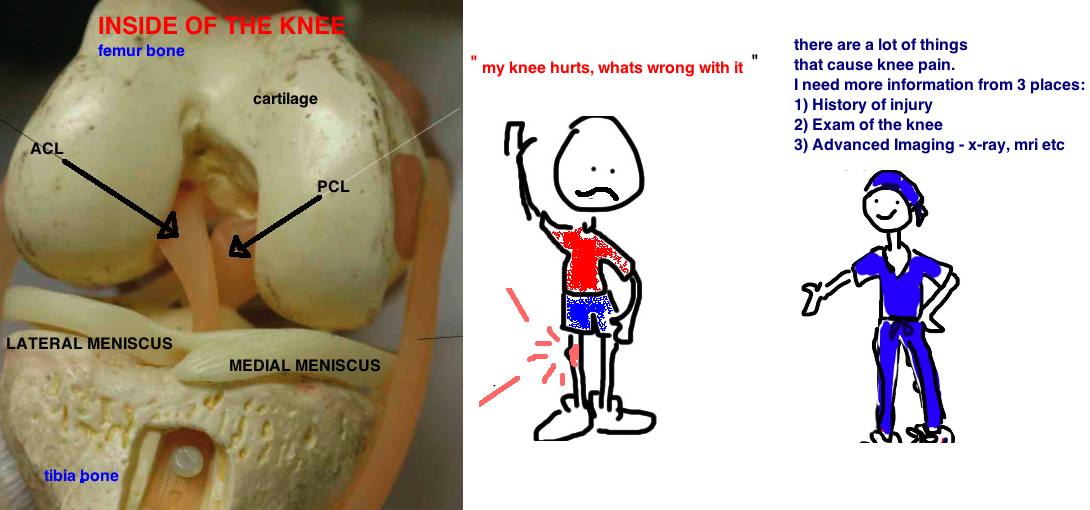
We are going to focus on sports injuries to the knee - including meniscus tear, ACL tear, cartilage injury and other ligament injuries.
Diagnosing a problem is based on first gathering information. The information for knee injuries comes from 3 sources - 1) History of injury; 2) Examination of the knee; 3) X-rays and MRIs.
1) HISTORY OF INJURY
90% of injuries can be diagnosed by listening to the history of the injury and asking the correct questions.
The meniscus is an important structure in the knee, its made from the same proteins as cartilage, but it is a crescent disc that sits just above the cartilage and helps as a shock absorber, joint stabilizer, increasing surface area for stresses, centers the knee, and helps with lubrication of the knee. Meniscus tears in 2 ways - 1) during activity when someone twists their knee when its semi-bent, 2) over time the meniscus starts to degenerate, particularly in people with mild to moderate arthritis. Meniscus tears people often don't remember the incident when it occurred, they report feeling "fuzzy" discomfort in their knee, pain with squatting, and clicking and occasional locking in their knee. The knee can get swollen after a busy day, but the knee does not swell to the size of a grapefruit.
The ACL is a ligament in the center of the knee and it stabilizes the leg from shift forward during cutting and pivoting activity. The ACL tears during a sharp pivoting motion, when the knee is bent inward. ACL tears people almost always remember the moment it happens - pivot on the leg, then feel a pop in the knee, immediately it becomes very swollen. After the injury the knee feels unstable.
Cartilage injury people occasionally remember the incident when the banged their knee, but they report similar issues to meniscus tear - occasional locking in their knee, localized knee pain, gets swollen after busy day.
2) EXAM OF KNEE
Meniscus exam attempts to re-create the pain of having the flap of torn meniscus pinched. The McMurray test is the classic test which looks for tears in the back of the meniscus. The Apley grind test puts axial force on the bent knee (90 degrees) then rotates the knee to elicit pain. The Thessaly test has a person stand one leg (affected knee) bend the knee slightly and then twist their body back and forth to cause pain. While all of these tests are helpful, a recent study combining many studies, showed they tests are only 60% accurate in diagnosing a tear.
ACL exam looks for knee instability by pulling the shin bone forward while stabilizing the thigh bone. A normal ACL will prevent the knee from shifting forward with this maneuver (called a Lachman exam), a pivot shift test similarly puts a stress on the knee (similar to the one that caused the injury) and sees if the knee is loose.
Cartilage injury - The most common place is behind the kneecap. One test is to have a person lie on their back and put pressure on the knee cap to see if it causes sharp pain (sees pretty obvious, right?). However this test is not very accurate. Because kneecap instability can be a major cause of cartilage injury, tests for kneecap instability like measuring the Q angle, looking for the J sign, and Fairbanks can help in looking for cartilage injury but these tests are also not super accurate. The Wilson test looks at how patients walk when they have a cartilage injury on the inside of their knee, and this test can be moderately helpful.
3) IMAGING
Meniscus tear - despite the relative inaccuracy of the exam tests described above, many doctors feel that when performed in combination, these tests become very accurate and don't require MRI for diagnosis... they will take patients for an arthroscopic meniscus cleaning or repair without an MRI.
ACL tear - the examination of the ACL is fairly accurate and therefore, some doctors will take a patient for surgery without getting an MRI, most however, will get an MRI to see if there is any injury to the meniscus so that they can plan to fix that as well. Its more difficult to diagnose a torn meniscus on top of an ACL tear because the ACL tear disguises injuries to the rest of the knee.
Cartilage injury - X-rays are good an showing injuries to the bone but they are not good at showing injuries to cartilage or ligaments. Also because cartilage injuries do not have reliable exam findings, MRIs are very useful in the diagnosis of these injuries.
REFERENCES
McMurray TP: The semilunar cartilages. Br J Surg 1942;29(116):407–414.
Rayan F, Bhonsle S, Shukla DD: Clinical, MRI, and arthroscopic correlation in meniscal and anterior cruciate ligament injuries. Int Orthop 2009;33(1):129–132. dont need MRI to book arthroscopy.
Kocabey Y, Tetik O, Isbell WM, Atay OA, Johnson DL: The value of clinical examination versus magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of meniscal tears and anterior cruciate ligament rupture. Arthroscopy 2004;20(7):696–700. clinical exam is as good as mri.
Pihlajamäki HK, Kuikka PI, Leppänen VV, Kiuru MJ, Mattila VM: Reliability of clinical findings and magnetic resonance imaging for the diagnosis of chondromalacia patellae. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2010;92(4):927–934. no good exam test for patellar chondromalacia.
Smith TO, Clark A, Neda S, et al: The intra- and inter-observer reliability of the physical examination methods used to assess patients with patellofemoral joint instability. Knee 2012;19(4):404–410. no reliable exam for patellar instability.
Wilson JN: A diagnostic sign in osteochondritis dissecans of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1967;49(3):477–480. sign of OCD lesions